2014 June UGC NET Paper 1
Question 1 |
Break-down in verbal communication is described as
Short Circuit | |
Contradiction | |
Unevenness | |
Entropy |
Question 2 |
The Telephone Model of Communication was first developed in the area of
Technological theory | |
Dispersion theory | |
Minimal effects theory | |
Information theory |
Question 3 |
The Dada Saheb Phalke Award for 2013 has been conferred on
Karan Johar | |
Amir Khan | |
Asha Bhonsle | |
Gulzar |
Question 4 |
Photographs are not easy to
Publish | |
Secure | |
Decode | |
Change |
Question 5 |
The grains that appear on a television set when operated are also referred to as
Sparks | |
Green Dots | |
Snow | |
Rain Drops |
Question 6 |
In circular communication, the encoder becomes a decoder when there is
Noise | |
Audience | |
Criticality | |
Feedback |
Question 7 |
In a post-office, stamps of three different denominations of Rs 7, Rs 8, Rs 10 are available. The exact amount for which one cannot buy stamps is
19 | |
20 | |
23 | |
29 |
Question 7 Explanation:
Option B: 10 * 2=20
Option C: 7+8+8=23
Option D: 7+7+7+8=29
Question 8 |
In certain coding method, the word QUESTION is encoded as DOMESTIC. In this coding, what is the code word for the word RESPONSE?
OMESUCEM | |
OMESICSM | |
OMESICEM | |
OMESISCM |
Question 8 Explanation:

Question 9 |
If the series 4,5,8,13,14,17,22,........ is continued in the same pattern, which one of the following is not a term of this series?
31 | |
32 | |
33 | |
35 |
Question 10 |
Complete the series BB, FE, II, ML, PP: ..:........by choosing one of the following option given :
TS | |
ST | |
RS | |
SR |
Question 10 Explanation:
BB, FE, II, ML, PP, TS
After B we leave 3 and reach to F.
Similarly, after P leave 3 and reach T and one behind is S.
Answer will be TS.
After B we leave 3 and reach to F.
Similarly, after P leave 3 and reach T and one behind is S.
Answer will be TS.
Question 11 |
A man started walking frorn his house towards south. After walking 6 km, he turned to his left walked 5 Km after. Then he walked further 3 km after turning left. He then turned to his left and continued his walk for 9 km. How far is he away from his house?
3 km | |
4 km | |
5 km | |
6 km |
Question 11 Explanation:
C2=42+32
C2=25
C=5
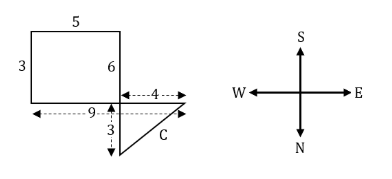
C2=25
C=5

Question 12 |
One writes all numbers from 50 to 99 without the digits 2 and 7. How many numbers have been written?
32 | |
36 | |
40 | |
38 |
Question 13 |
"If a large diamond is cut up into little bits it will lose its value just as an army is divided up into small units of soldiers. It loses its strength." The argument put above may be called as
Analogical | |
Deductive | |
Statistical | |
Casual |
Question 13 Explanation:
The given argument can be called as analogical.
→ Analogical arguments are a form of induction where a conclusion is derived from a comparison of similarities between two (or) more cases.
→ Analogical arguments are a form of induction where a conclusion is derived from a comparison of similarities between two (or) more cases.
Question 14 |
Given below are some characteristics of logical argument. Select the code which expresses a characteristic which is not of inductive in character.
The conclusion is claimed to follow from its premises. | |
The conclusion is based on causal relation. | |
The conclusion conclusively follows from its premises. | |
The conclusion is based on observation and experiment |
Question 14 Explanation:
Inductive reasoning is a method of reasoning in which the premises are viewed as supplying some evidence for the truth of the conclusion and this is in contrast to deductive reasoning.
Question 15 |
If two propositions having the same subject and predicate terms can both be true but cannot both be false, the relation between those two propositions is called
contradictory | |
contrary | |
subcontrary | |
subaltern |
Question 15 Explanation:
Subcontrary:- Denoting the preposition can be true but cannot be false.
There are 15 questions to complete.
